Inspect
sq inspect
inspects metadata (schema/structure, tables, columns) for a source,
or for an individual table. When used with --json, the output of sq inspect can
be fed into other tools such as jq
to enable complex data pipelines.
Let’s start off with a single source, a Postgres Sakila database:
# Start the Postgres container
$ docker run -d -p 5432:5432 sakiladb/postgres:12
# Add the source
$ sq add postgres://sakila:p_ssW0rd@localhost/sakila --handle @sakila_pg
@sakila_pg postgres sakila@localhost/sakila
Inspect source
Use sq inspect @sakila_pg to inspect the source.
You can also use sq inspect with stdin, e.g.:
$ cat actor.csv | sq inspect
However, note that stdin sources can’t take advantage of ingest caching
, because
the stdin pipe is “anonymous”, and sq can’t do a cache lookup for it. If you’re going to
repeatedly inspect the same stdin data, you should probably just sq add
it.
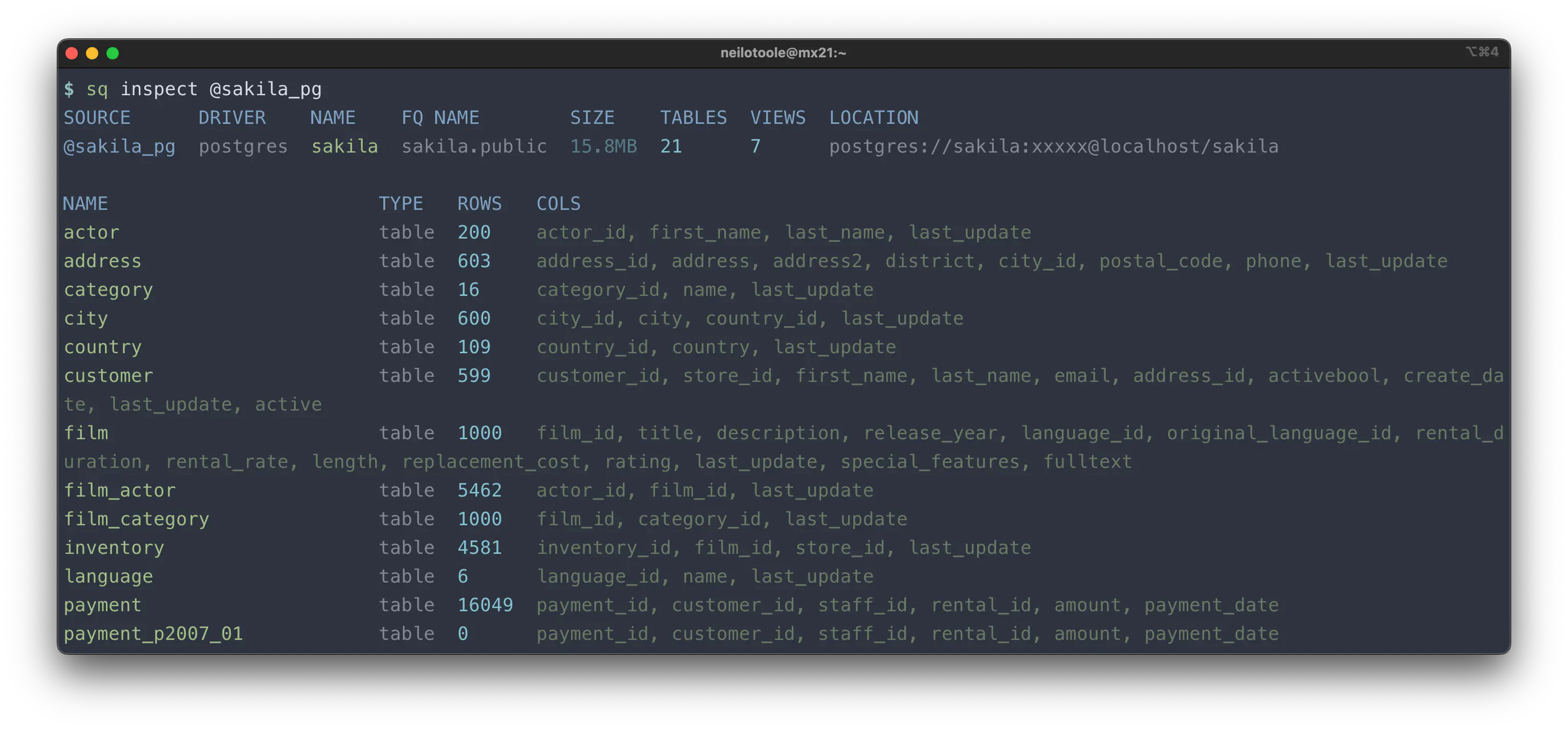
This output includes the source metadata, and the schema structure (tables, columns, etc.).
--text (default)
$ sq inspect @sakila_pg
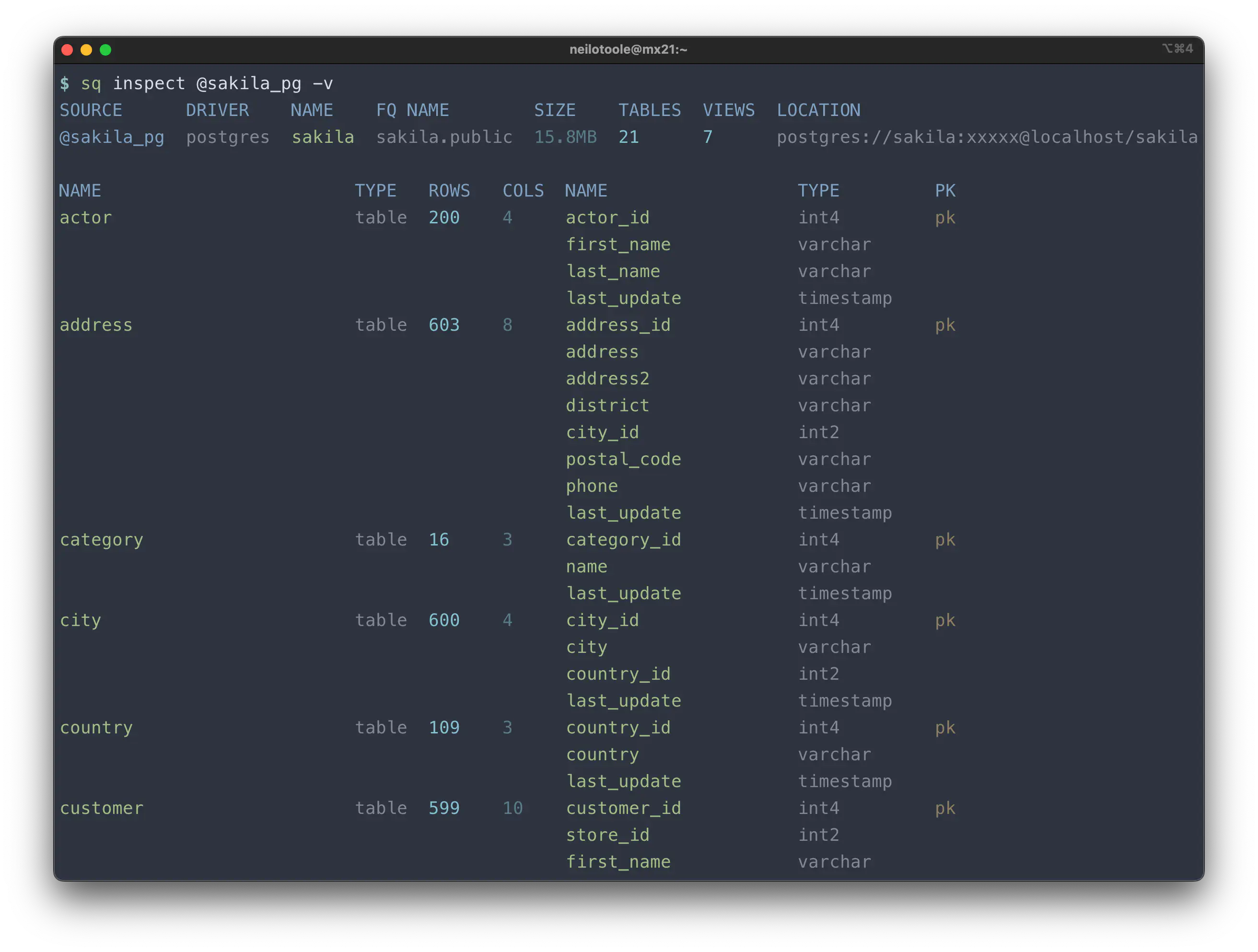
--verbose
To see more detail, use the --verbose (-v) flag with the --text format.
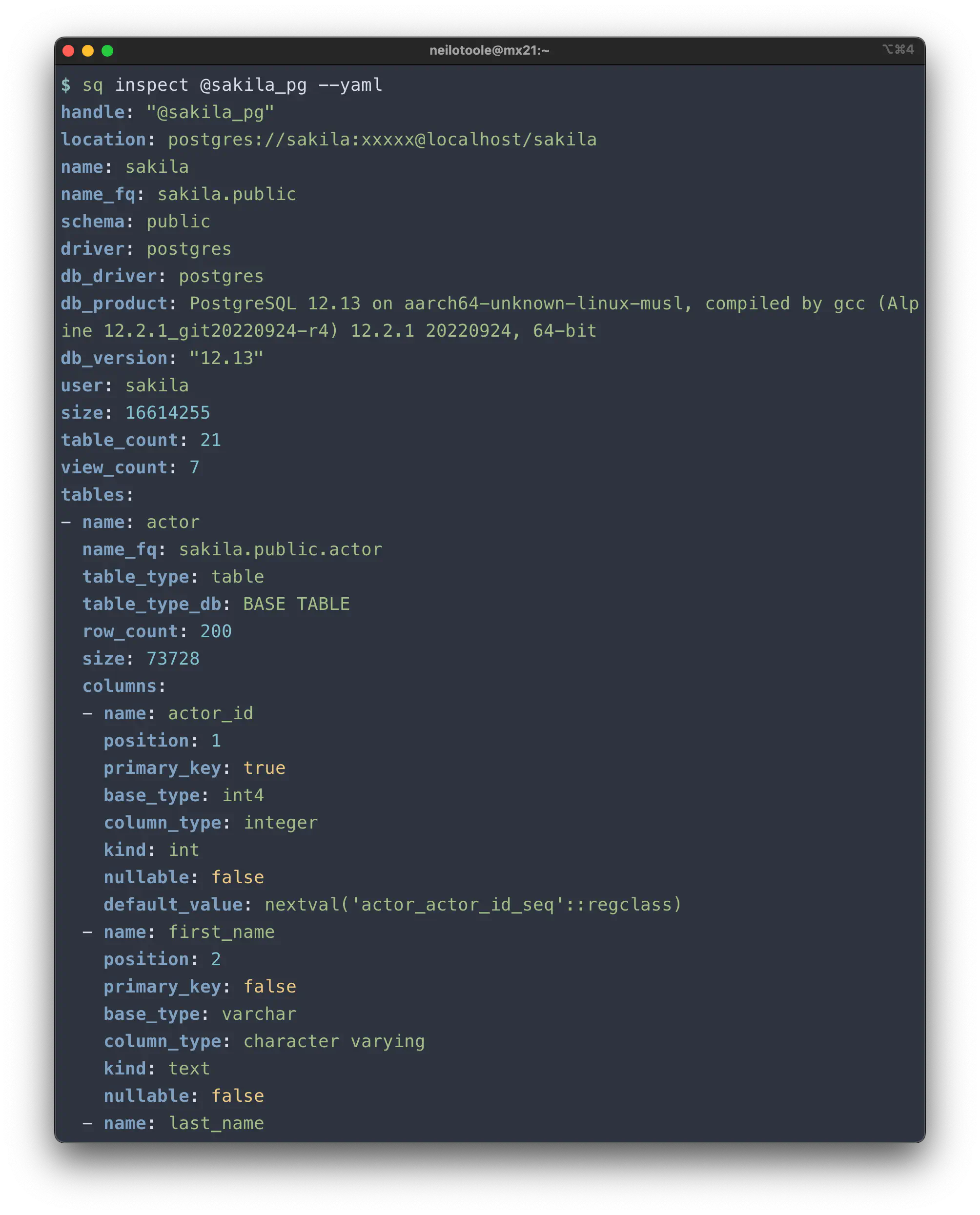
--yaml
To see the full output, use the --yaml (-y) flag. YAML has the advantage
of being reasonably human-readable.
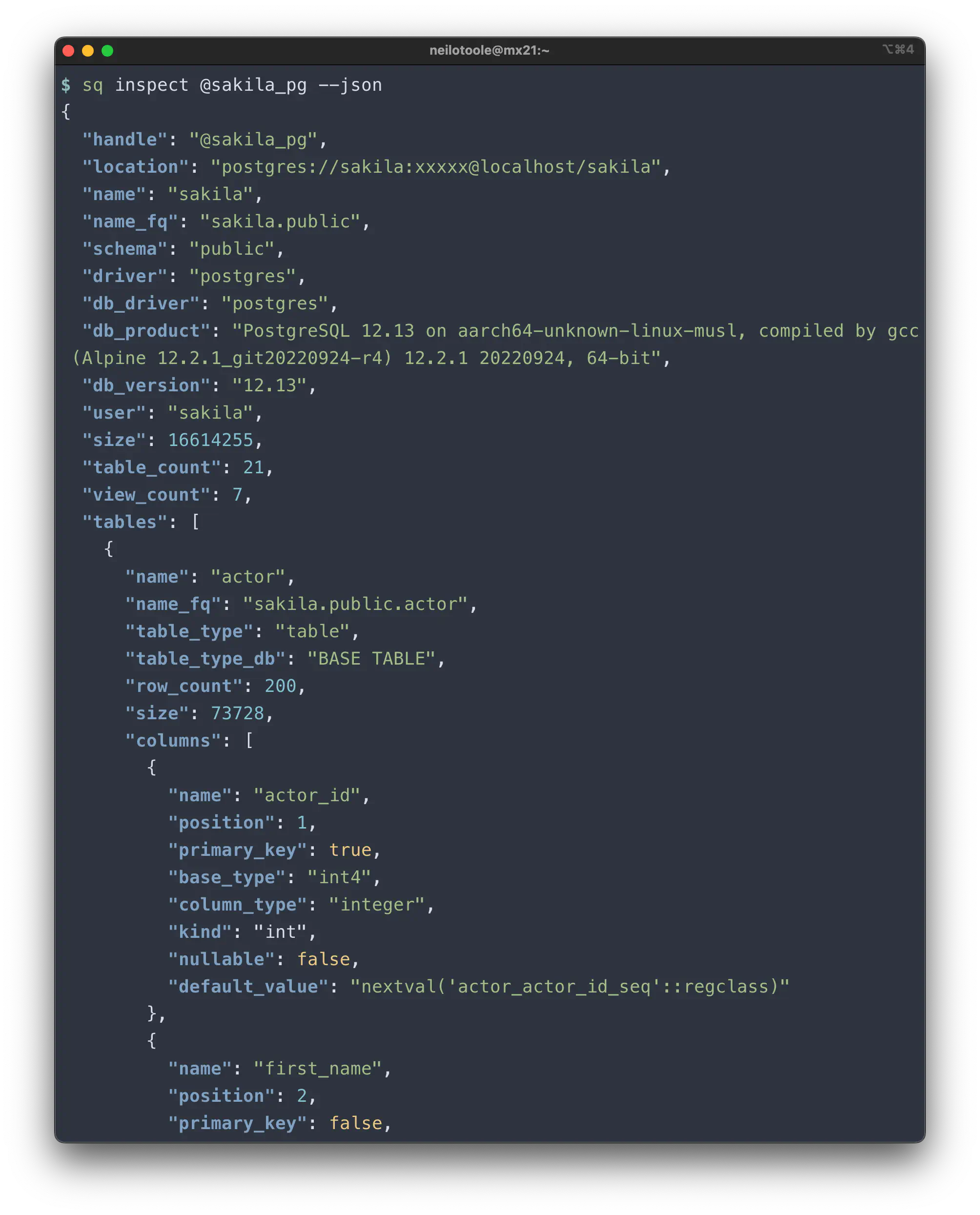
sq to introspect the schema.--json
The --json (-j) format renders the same content as --yaml, but is more
suited for use with other tools, such as jq
.
Here’s an example of using sq with jq to list all table names:
$ sq inspect -j | jq -r '.tables[] | .name'
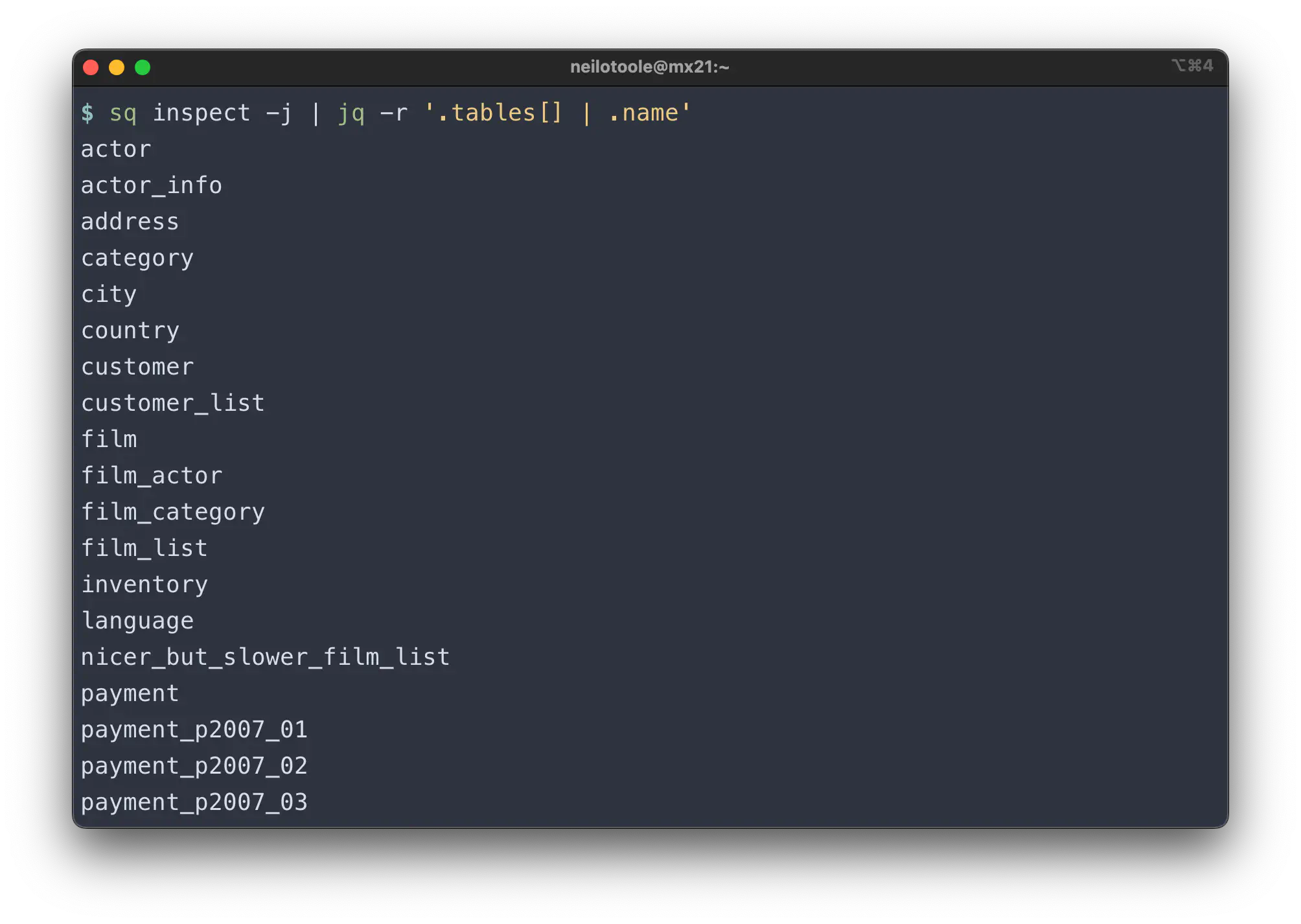
See more examples in the cookbook .
Source overview
Sometimes you don’t need the full schema, but still want to view the source
metadata. Use the --overview (-O) mode to see just the top-level metadata.
This excludes the schema structure, and is also much faster to complete.
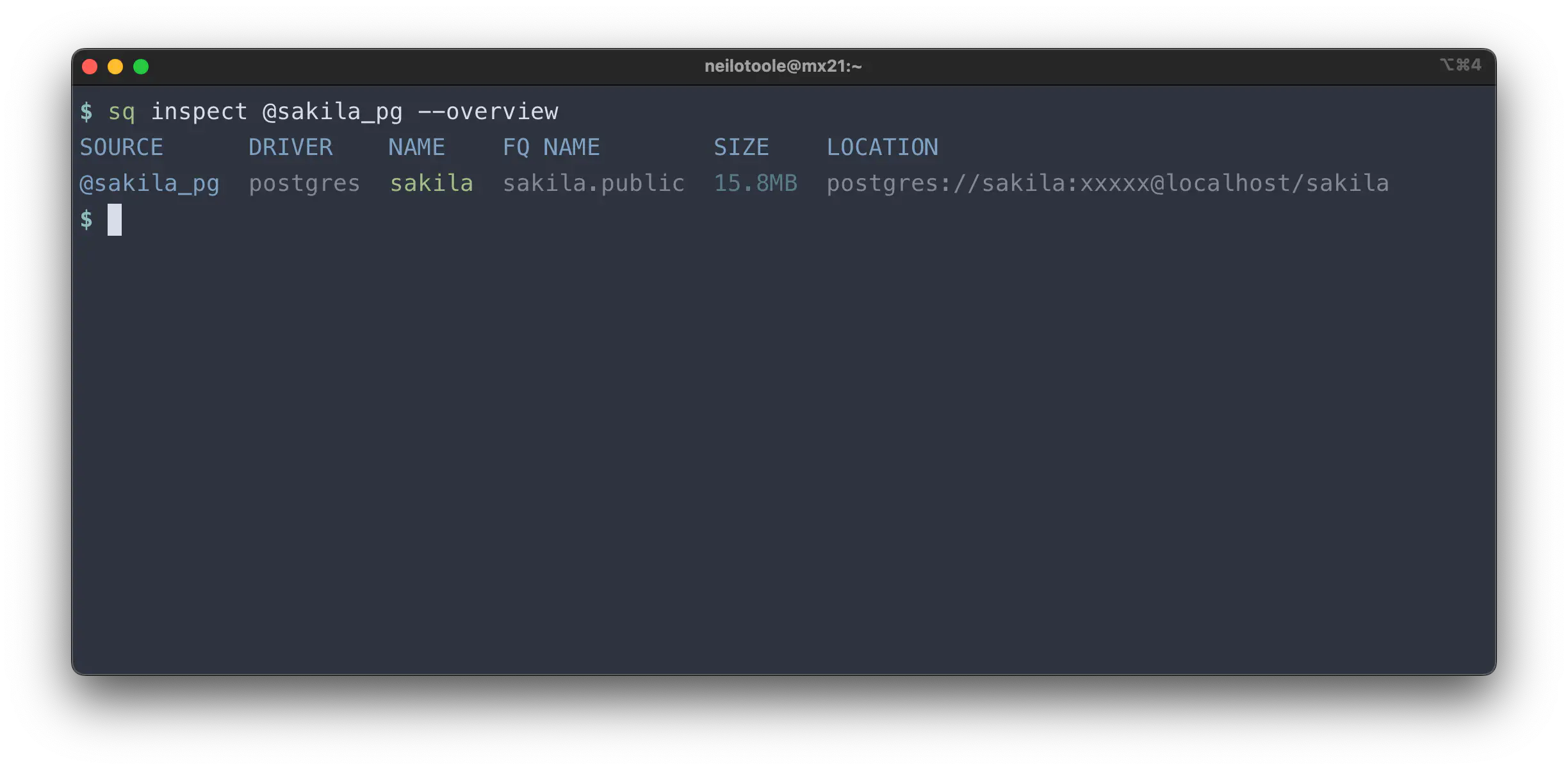
Well, that’s not a lot of detail. The --yaml output is more useful:
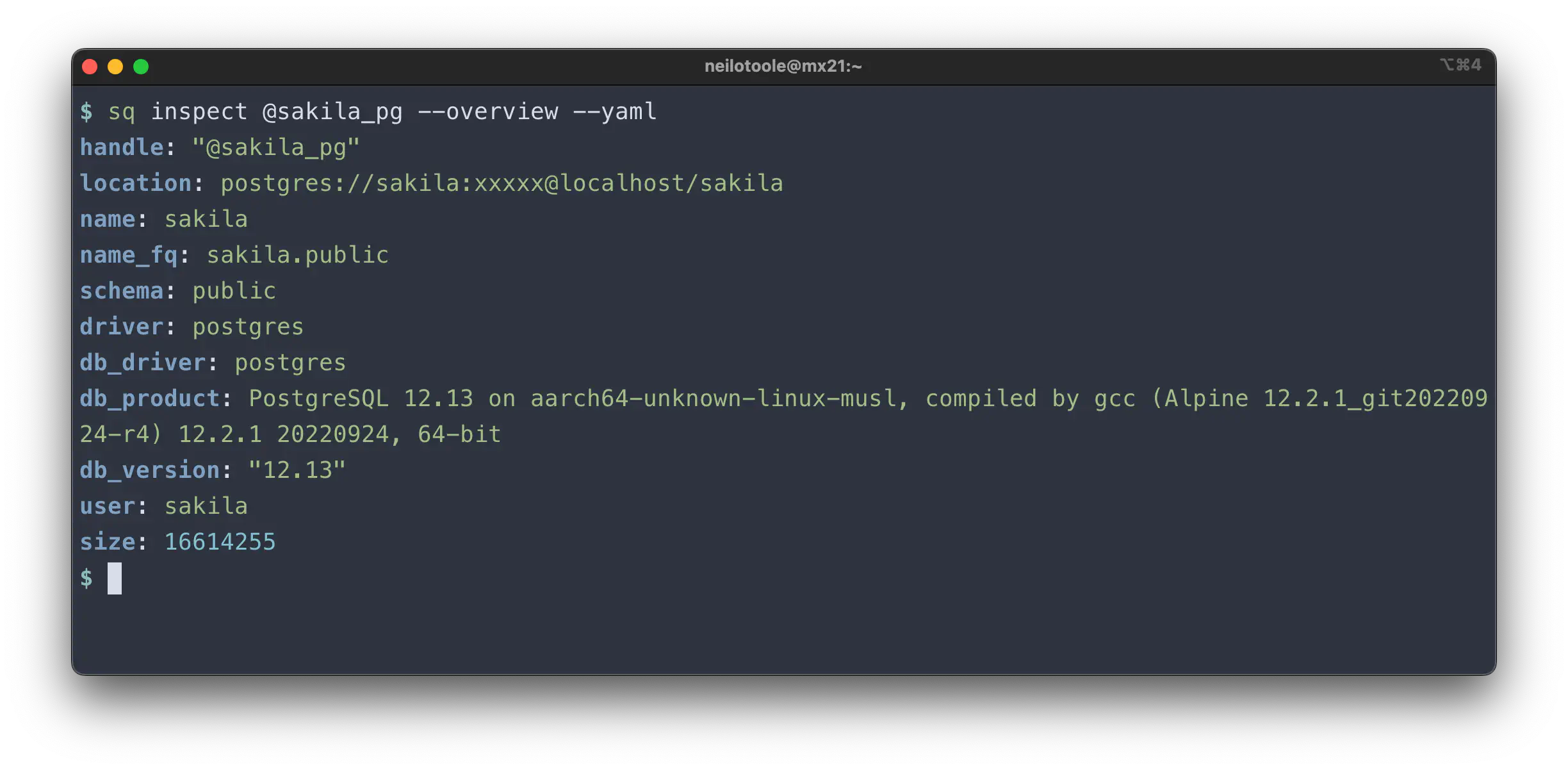
The --json format produces similar output.
Database properties
The --dbprops mode displays the underlying database’s properties, server config,
and the like.
$ sq inspect @sakila_pg --dbprops
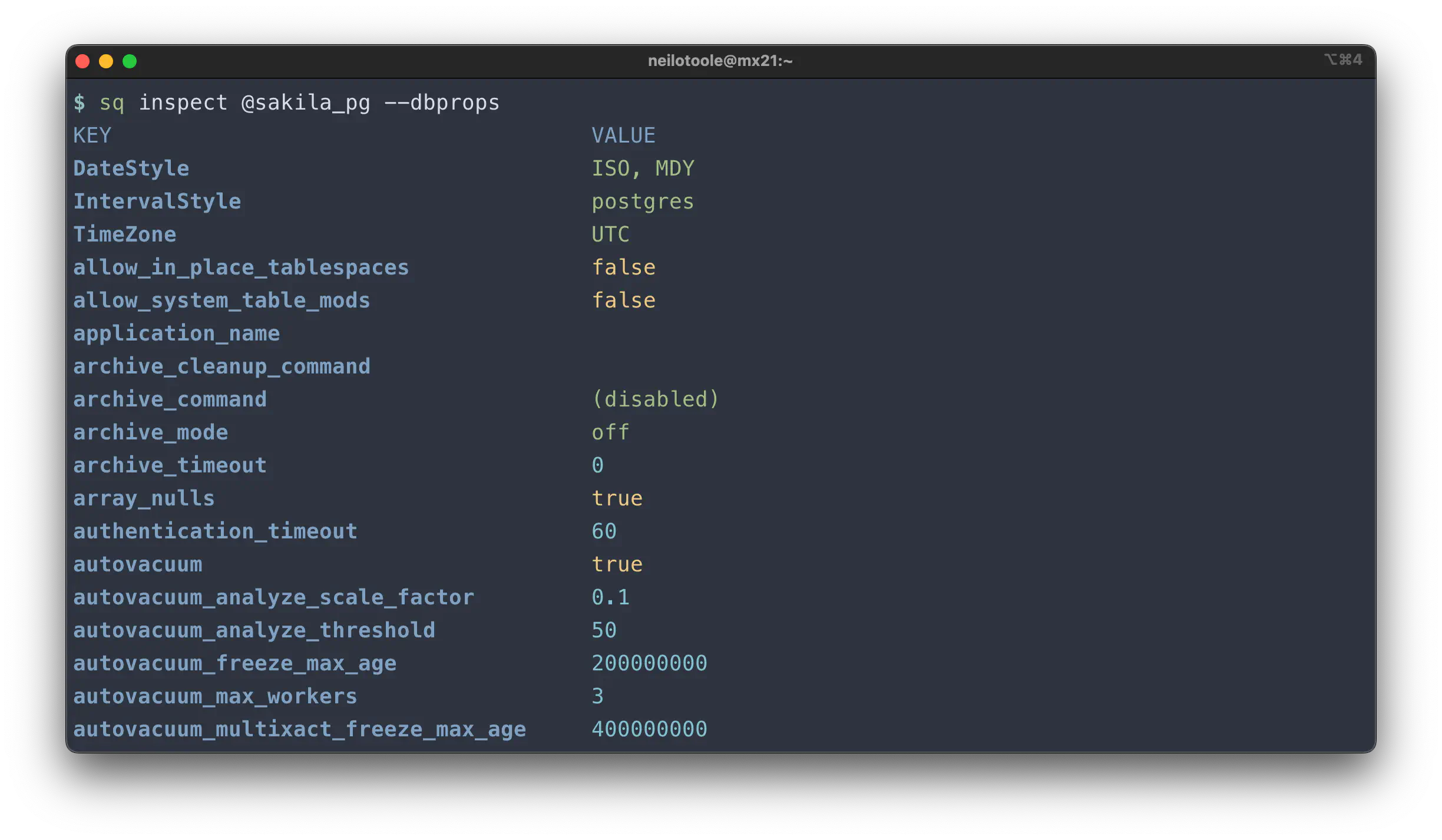
Use --dbprops with --yaml or --json to get the properties in machine-readable
format. Note that while the returned structure is generally a set of key-value
pairs, the specifics can vary significantly from one driver type to another.
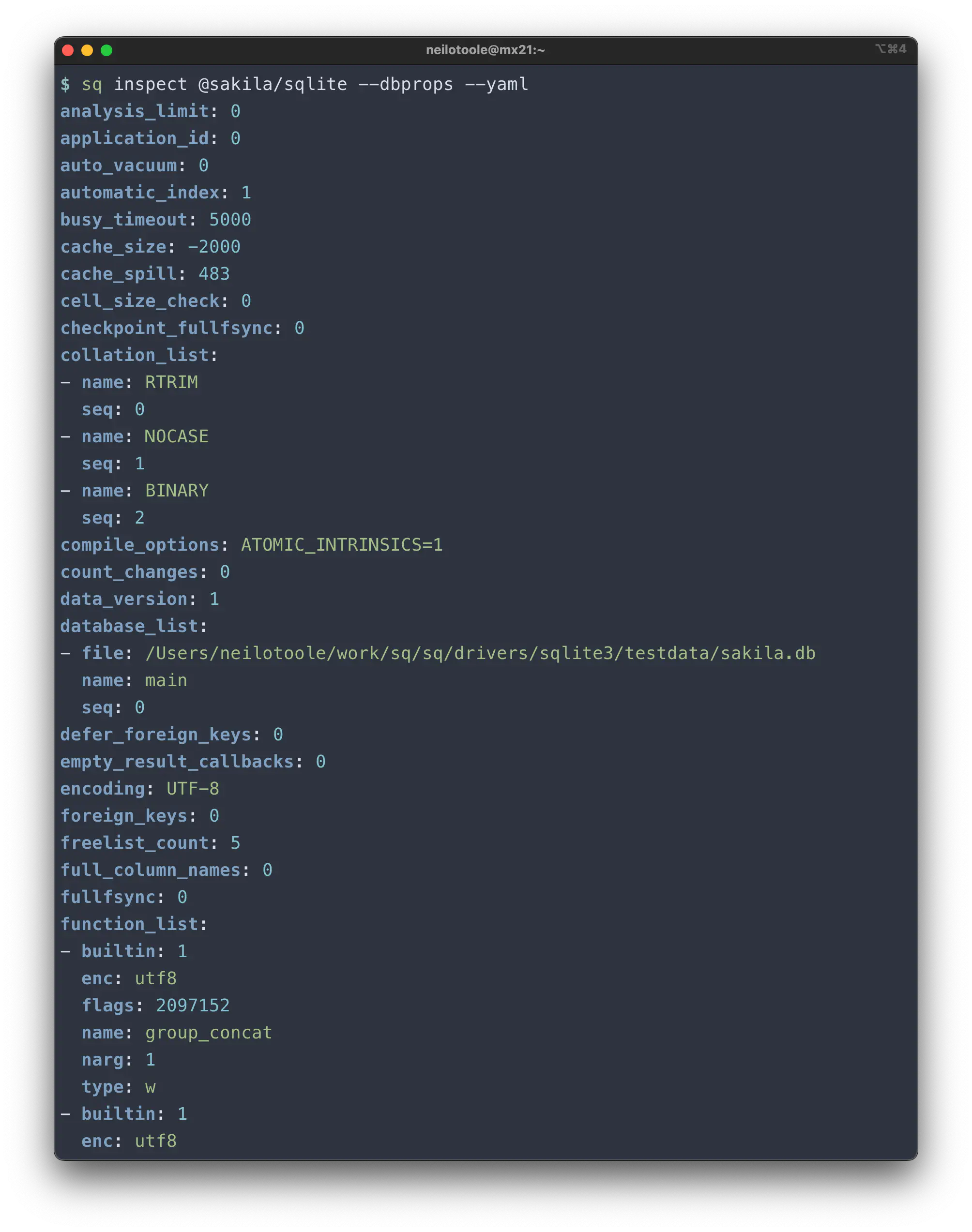
Here’s --dbprops from a SQLite
database (in --yaml format):
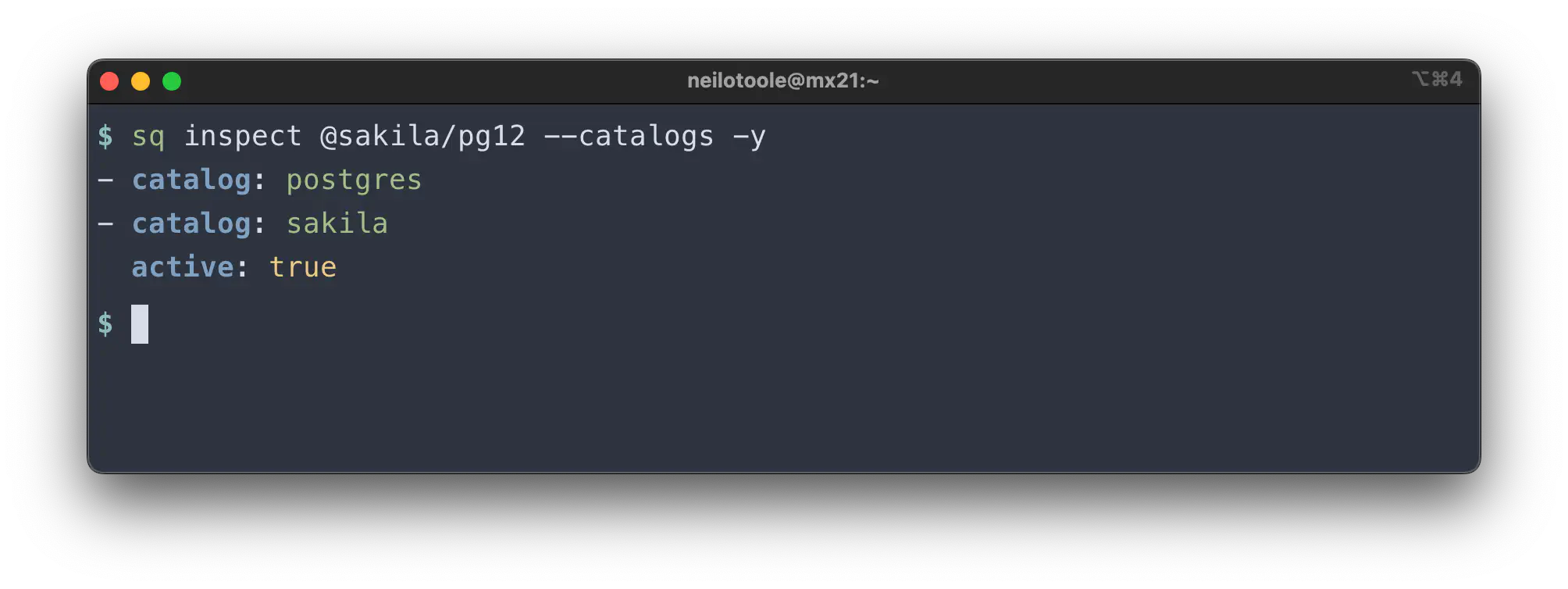
Catalogs
The --catalogs mode lists the catalogs
(databases)
available in the source.
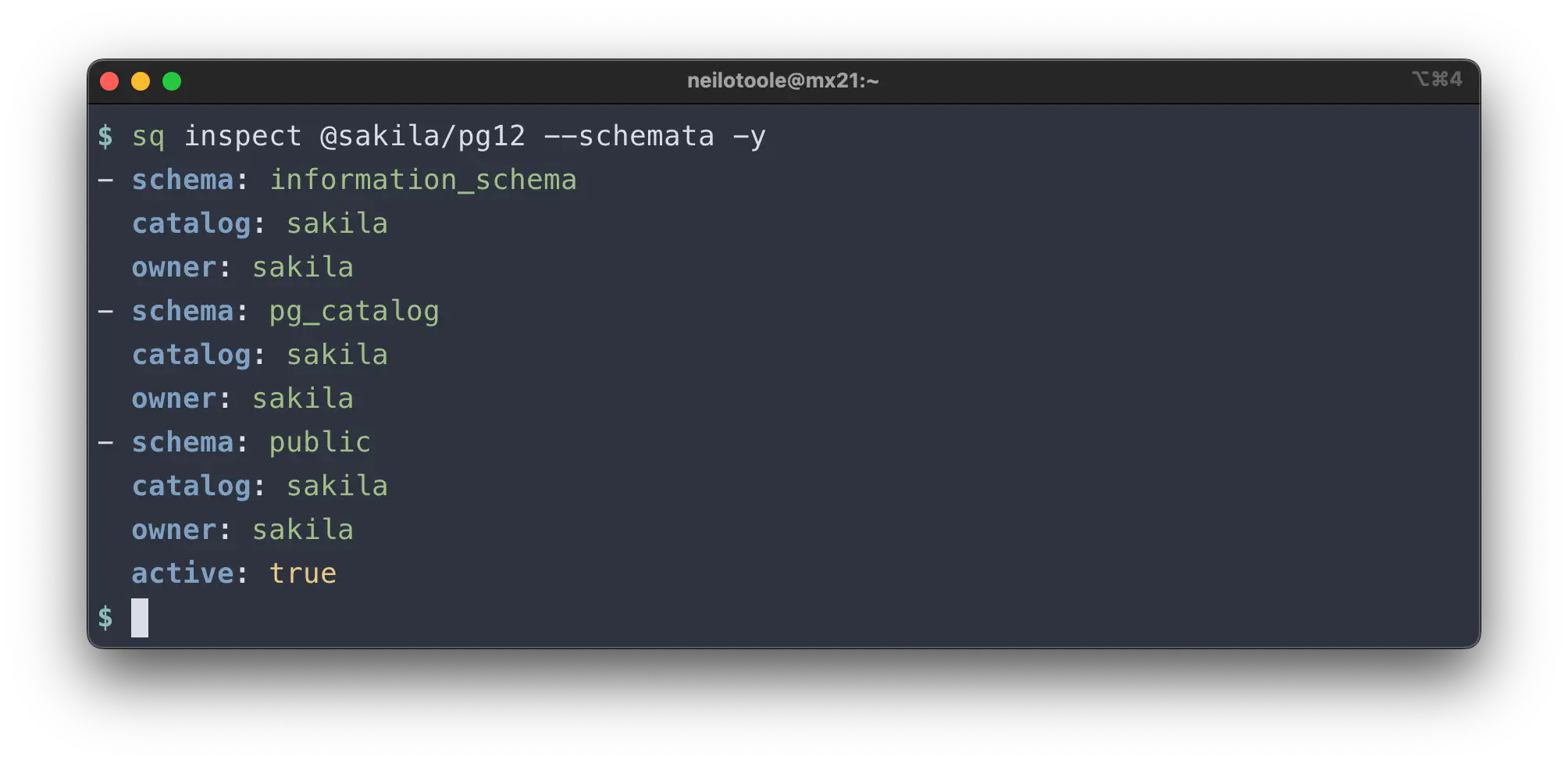
Schemata
Like --catalogs, the --schemata mode lists the schemas
available in the source.
To list the schemas in a specific catalog, supply CATALOG. to the
--src.schema
flag:
# List the schemas in the "inventory" catalog.
$ sq inspect @sakila/pg12 --schemata --src.schema inventory.
Inspect table
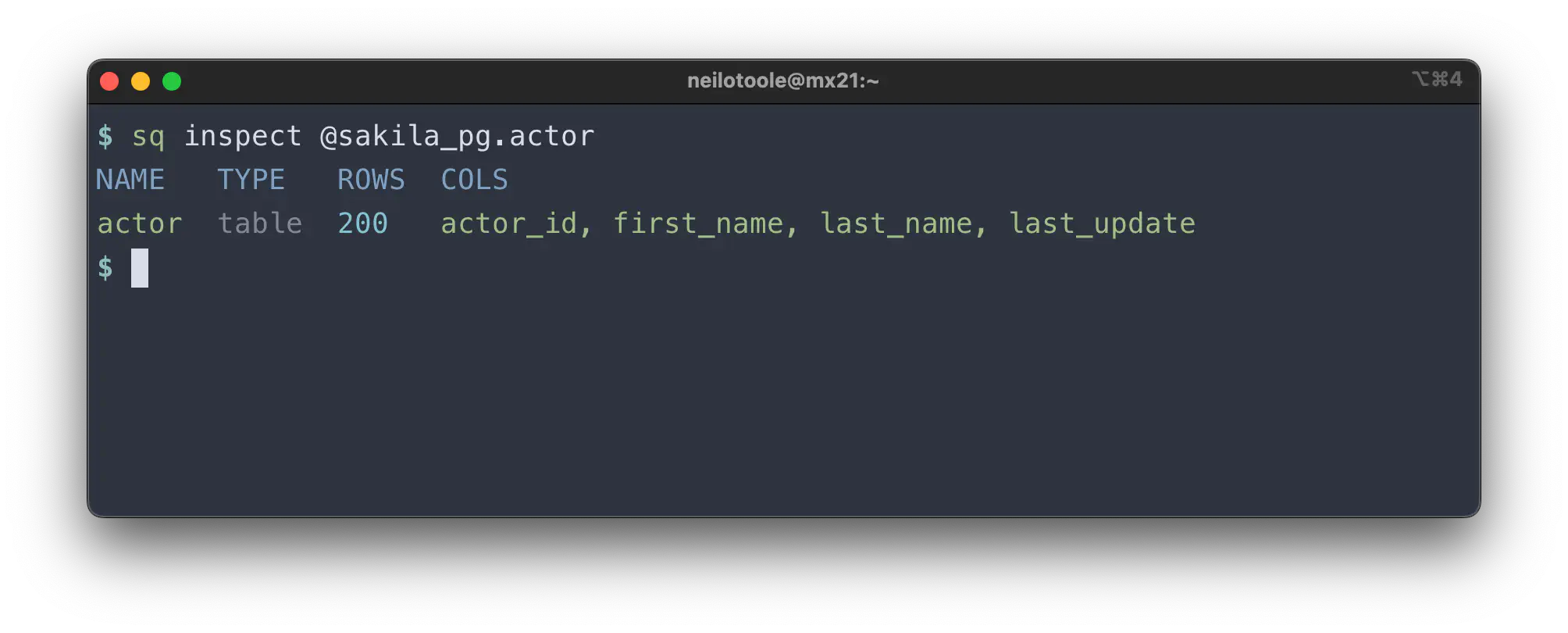
In additional to inspecting a source, you can drill down on a specific table.
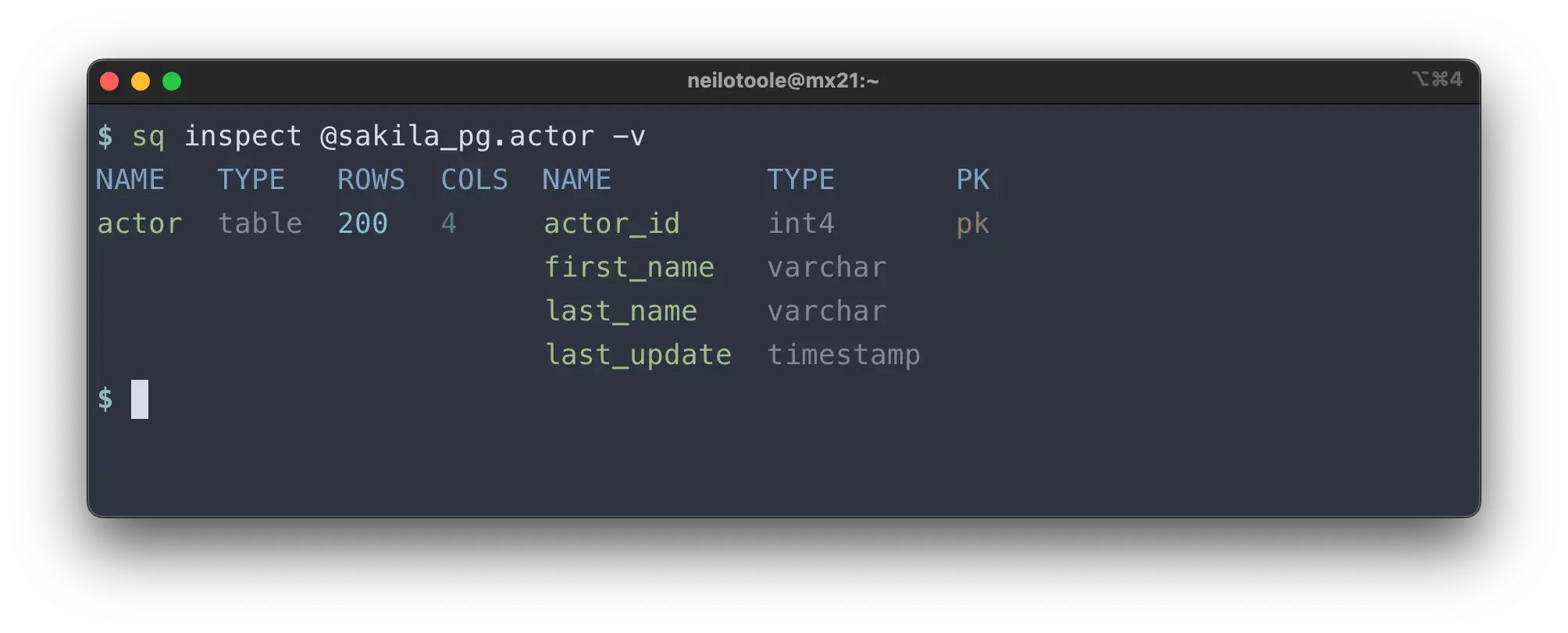
$ sq inspect @sakila_pg.actor
Use --verbose mode for more detail:
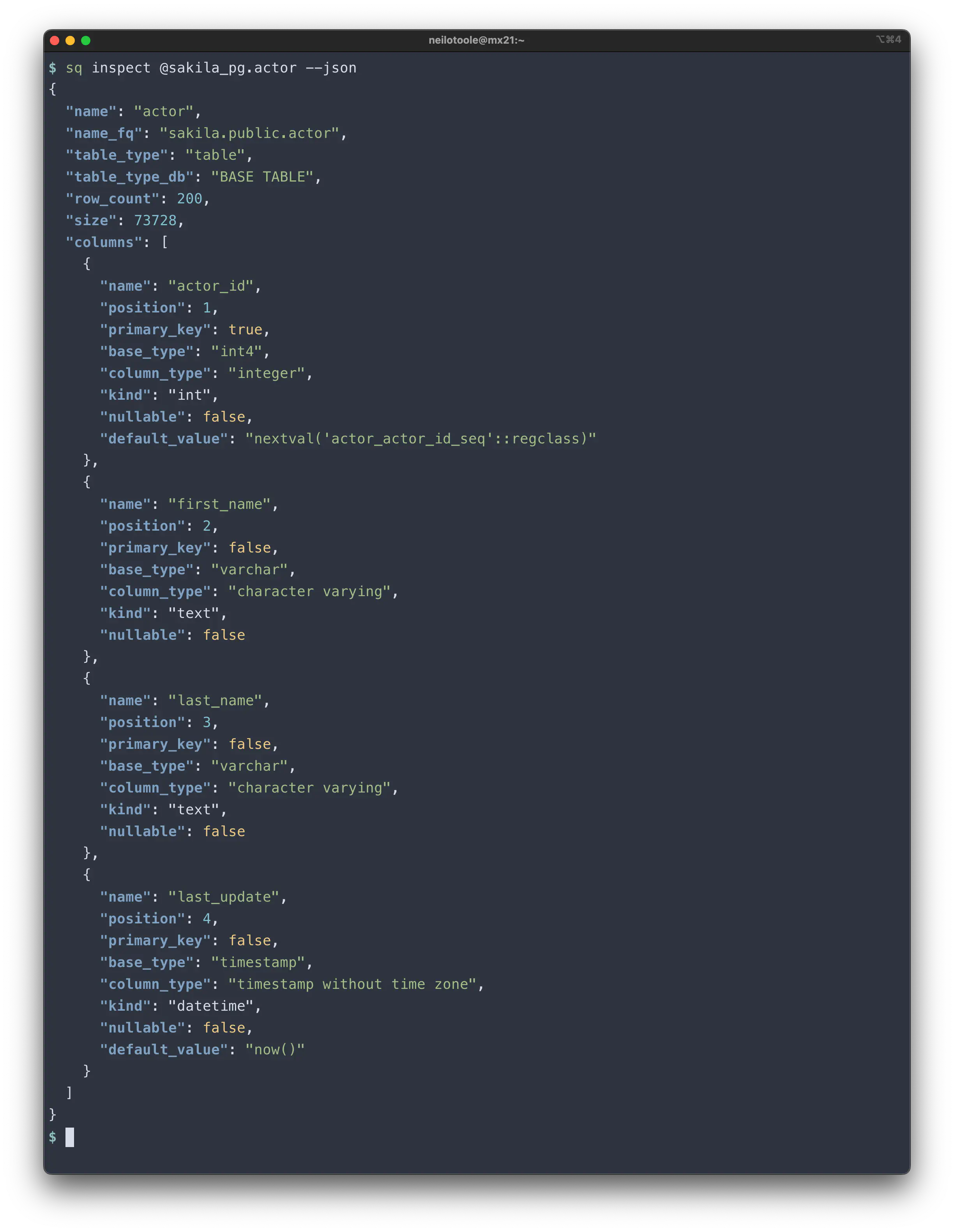
And, as you might expect, you can also see the output in --json and --yaml formats.
--overview and --dbprops flags apply only to inspecting sources,
not tables.Override active schema
By default, sq inspect uses the active schema
for the source. You can override the active schema (and catalog)
using the --src.schema
flag. See the sources
section
for a fuller explanation of --src.schema, but here’s a quick example of
inspecting Postgres’s information_schema schema:
$ sq inspect @sakila/pg12 --src.schema sakila.information_schema
SOURCE DRIVER NAME FQ NAME SIZE TABLES VIEWS LOCATION
@sakila/pg12 postgres sakila sakila.information_schema 16.6MB 7 61 postgres://sakila:xxxxx@192.168.50.132/sakila
NAME TYPE ROWS COLS
sql_features table 716 feature_id, feature_name, sub_feature_id, sub_feature_name, is_supported, is_verified_by, comments
sql_implementation_info table 12 implementation_info_id, implementation_info_name, integer_value, character_value, comments
sql_languages table 4 sql_language_source, sql_language_year, sql_language_conformance, sql_language_integrity, sql_language_implementation, sql_language_binding_style, sql_language_programming_language
sql_packages table 10 feature_id, feature_name, is_supported, is_verified_by, comments
sql_parts table 9 feature_id, feature_name, is_supported, is_verified_by, comments
sql_sizing table 23 sizing_id, sizing_name, supported_value, comments
sql_sizing_profiles table 0 sizing_id, sizing_name, profile_id, required_value, comments
_pg_foreign_data_wrappers view 0 oid, fdwowner, fdwoptions, foreign_data_wrapper_catalog, foreign_da